“Booting” is simply the process of starting up a computer. It’s what happens from the moment you press the power button until your computer is fully ready for you to use it – you see your desktop, or a login screen, and can open programs.
Imagine it like waking up in the morning: you don’t just instantly go from asleep to fully alert, dressed, and ready to work. There’s a sequence of events: your brain slowly kicks in, your body stretches, you get out of bed, get dressed, eat breakfast, and then you’re ready for the day. Booting is a similar, step-by-step process for a computer.
Let’s break it down in a simple way:
The Goal of Booting: To Load the Operating System
The main purpose of the booting process is to load the Operating System (OS) into the computer’s Random Access Memory (RAM). The OS (like Windows, macOS, or Linux) is the master program that manages all the computer’s hardware and software, allowing you to interact with it. Without the OS running, your computer is just a collection of inert parts.
Steps of Booting
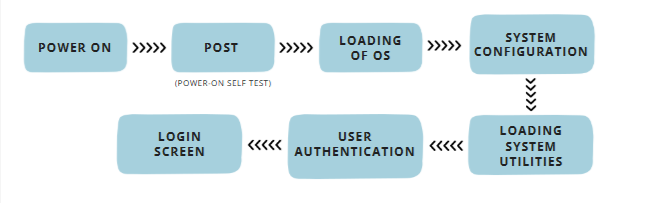
We can describe the boot process in six steps:
- The Startup : It is the first step that involves switching the power ON. It supplies electricity to the main components like BIOS and processor.
- BIOS : Power On Self Test : It is an initial test performed by the BIOS. Further, this test performs an initial check on the input/output devices, computer’s main memory, disk drives, etc. Moreover, if any error occurs, the system produces a beep sound.
- Loading of OS : In this step, the operating system is loaded into the main memory. The operating system starts working and executes all the initial files and instructions.
- System Configuration : In this step, the drivers are loaded into the main memory. Drivers are programs that help in the functioning of the peripheral devices.
- Loading System Utilities : System utilities are basic functioning programs, for example, volume control, antivirus, etc. In this step, system utilities are loaded into the memory.
- User Authentication : If any password has been set up in the computer system, the system checks for user authentication. Once the user enters the login Id and password correctly the system finally starts.
Types of Booting
There are two types of booting:
- Cold Booting : A cold boot is also called a hard boot. It is the process when we first start the computer. In other words, when the computer is started from its initial state by pressing the power button it is called cold boot. The instructions are read from the ROM and the operating system is loaded in the main memory.
- Warm Booting : Warm Boot is also called soft boot. It refers to when we restart the computer. Here, the computer does not start from the initial state. When the system gets stuck sometimes it is required to restart it while it is ON. Therefore, in this condition the warm boot takes place. Restart button or CTRL+ALT+DELETE keys are used for warm boot.
